Food traceability on the blockchain: LTO Network
Food traceability through supply chains with blockchain is a hot topic in the blockchain landscape. Many have tried to solve the issues that arise when sharing data as a consortium, and almost as many have failed trying so. LTO Network came up with a solution, and – because it could be done in 48 hours at the Odyssey Hackathon – build the solution while we’re at it.
How does our solution look? Check out the video at the bottom of the article. But before that, let’s give some background information on (food) supply chains and how you can implement food traceability on the blockchain.
Current problems with the food supply chain
The food supply chain is one of the most complex and fragmented of all supply chains. The production is found all over the world, making many producers and intermediaries difficult to identify and track.
This brings uncertainty and risk to all stakeholders in the production chain. Because the production is so siloed and fragmented, fraud and counterfeiting are some very real problems facing the industry.
This, in turn, makes the whole food supply chain unfair for some stakeholders, not at all a level playing field for participants.
How blockchain can help
Every supply chain, therefore, needs blockchain, and enterprises are catching on. Leading players are already exploring ways to capture value from blockchain technology. Examples are CMA CGM, Anheuser-Busch InBev and Maersk.
First, the basics. Blockchain is a decentralized database. However, a centralized database is already very effective at keeping track of things. This could help reduce the complexity and fragmentation of a supply chain. The problem with centralized databases is that they rely heavily on trust: you trust any actor which has access to or maintains the database to not alter any data.
This still leaves room for fraud and counterfeiting. This is where blockchain technology could really help, because of its decentralized nature. When a database is decentralized, multiple actors have a copy of its contents. This means that multiple copies of the same database exist. All of these copies are checked for consistency when writing a new transaction onto it. When one copy of the database does not match with other copies of that same database, the transaction will be rejected. Thus, altering any data without the consent of those actors is very, very difficult, if not impossible. This is the power of blockchain technology.
The benefits of food traceability on the blockchain
Now how could this help the food supply chain with traceability? As mentioned before, a centralized database already helps with solving complexity and fragmentation issues in a supply chain. But only a decentralized database, which is immutable, could help solve fraud and counterfeiting issues because its data cannot be manipulated.
Now combine this technology with the use of a unique identifier such as a barcode, QR code, or an RFID transmitter and you could accurately trace everything in your food supply chain while limiting the options to commit fraud. Compared to current technologies, blockchain can easily regulate who gets access to information about the products. Integration with more complex technology, like different kinds or more accurate sensors, could further expand the information available on a blockchain network.
Blockchain adoption
One major hurdle, however, is the actual adoption of blockchain. Considering the magnitude of the potential benefits, blockchain adoption by the supply chain industry has been slower than expected. This has two reasons: the highly fragmented chain as stated above, and limited trust in participants in the supply chain.
The fragmentation of the supply chain is both the reason why blockchain is desperately needed and why it is so hard to adopt. Such fragmentation makes the implementation of blockchain very labor intensive and thus not worthwhile. On top of the fragmented supply chain comes the very limited trust participants of that chain have in other participants.
This forms a major barrier to adoption as parties are reluctant to share information with each other in this competitive industry.
LTO Network & supply chain traceability
Our solution for food traceability
Together with our Ecosystem V partners, Capptions and SignRequest, LTO Network has built a food traceability app called FoodFlow for the Nutreco track at the Odyssey hackathon. It utilizes LTO Network’s blockchain. Nutreco makes protein food that is used to feed animals. They want to have everybody in the supply chain know that the food they eventually feed to humans at the end of the chain all checks out and is safe. This is of course where blockchain comes in.
The solution consists of two workflows: the KYC & certification flow and the check for license & supply chain flow. The KYC flow is for registering every organization that is connected to the supply chain. They register and receive a license. Because this is a separate flow, all licenses can be revoked at any time during the process. Next is the supply chain flow, which is visualized below:
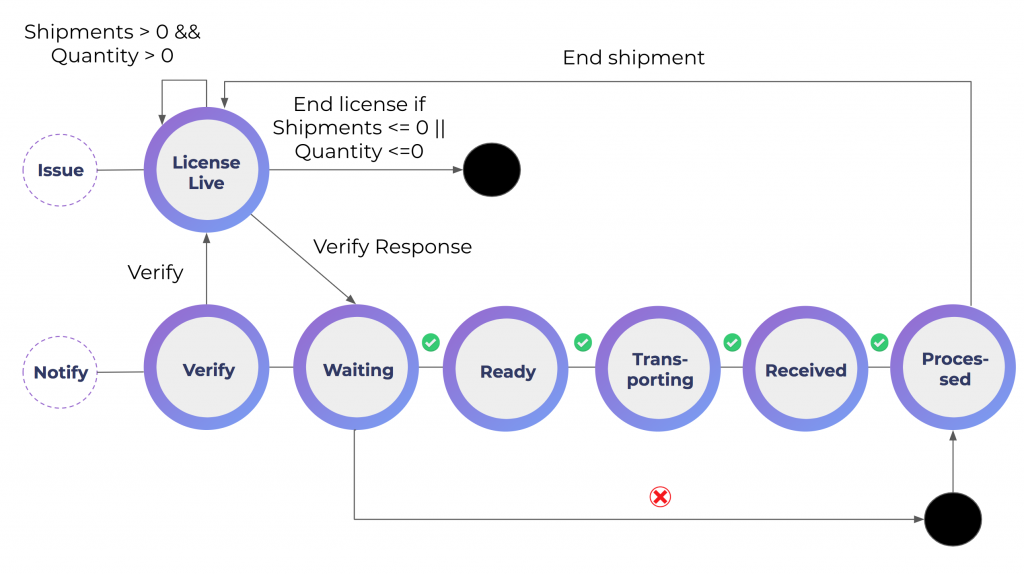
The flow starts by verifying if an actor has the license necessary to begin the flow. If it does not have the required license, the flow ends. However, if it does have the required license, the flow can proceed. From here all steps within the supply chain can be added and customized to reflect the supply process.
At any step, all parties have the ability to check the chain for verified data, like quantity, weight or location. Capptions has incorporated both workflows in their app, so everything is as easy to use as possible while benefiting from blockchain technology.
This has a few benefits. Almost all data that is added manually can be automated. Licenses can be revoked, on-chain. Your whole supply chain can go paperless, saving a lot of time and money. No use of slow ‘legacy’ blockchains or smart contracts.
All this is GDPR compliant by LTO Network’s design. And best of all: every organization in the world can very easily link their systems to this platform by setting up their own node and being invited to any workflow in which their actions are required. You can find more information about the use cases here.
Why LTO Network?
So why is LTO Networks solution different than any solution already out there? This answer is two-fold and is because of the way the network is set up.
A level playing field for all actors
First, the network is a private permissionless one. This means that it has the advantages of both private and permissionless blockchains. It remains censorship-resistant with trustless execution, which is only possible due to the decentralization of validators.
Basically, this means that no one party has control over another while ensuring the efficiency of the network. The whole chain is a level playing field. For competitors to sign on to your blockchain project, this is essential, as you can now easily onboard them. The onboarding of competitors is paramount to the survival of such a project.
Easy integration
Second, LTO Network is very easy to integrate with systems that are used right now. One example is out integration with SignRequest. Within a matter of minutes, you could add blockchain technology to your existing systems. LTO Network comes with its own API documentation. With just a simple API call you could be using LTO Network. With LTO Network being advantageous over other blockchain solutions in these ways, it solves the blockchain adoption hurdle as described above.
Conclusion
The gap between the physical product and the digital world needs to be better managed in order to foster adoption, efficiency, and transparency. Blockchain enables the integration of simple hardware and cheap software.
The prospect for food traceability on the blockchain and the supply chain industry is substantial. Using LTO Networks solution, businesses can very easily and affordably implement all the benefits blockchain technology has to offer. Using the app that is provided makes the solution very user-friendly, which significantly lowers the barrier to adopt the technology.
In our view, such an easy implementation process is essential in overcoming adoption issues. The food supply chain is in need of disruption and the easiest and most efficient way of doing that is with LTO Network. Together we work on the adoption of food traceability on the blockchain!
Learn more about how business can use the blockchain:
- Independent software vendors → Software applications which can anchor data on LTO Layer 1 public permissionless blockchain to secure the integrity of digital data. Here is a detailed business pitch.
- System integrators → Companies and providers utilizing LTO Layer 2 decentralized workflow engine to automate processes and solve the issues of data silos. Here is a detailed business pitch.
